Managing Django Settings: Issues
-
Different environments. Usually, you have several environments: local, dev, ci, qa, staging, production, etc. Each environment can have its own specific settings
-
Sensitive data. You have SECRET_KEY in each Django project. On top of this there can be DB passwords and tokens for third-party APIs like Amazon or Twitter. This data cannot be stored in VCS.
-
Sharing settings between team members. You need a general approach to eliminate human error when working with the settings.
- Django settings are a Python code. This is a curse and a blessing at the same time.
SSH:
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a remote administration protocol that allows users to control and modify their remote servers over the Internet.
- The service was created as a secure replacement for the unencrypted Telnet and uses cryptographic techniques to ensure that all communication to and from the remote server happens in an encrypted manner.
- It provides a mechanism for authenticating a remote user, transferring inputs from the client to the host, and relaying the output back to the client.
Understanding Different Encryption Techniques:
There are three different encryption technologies used by SSH:
Symmetric Encryption:
- Symmetric encryption is a form of encryption where a secret key is used for both encryption and decryption of a message by both the client and the host.
Asymmetric Encryption:
- Unlike symmetrical encryption, asymmetrical encryption uses two separate keys for encryption and decryption. These two keys are known as the public key and the private key. Together, both these keys form a public-private key pair.
Hashing
- One-way hashing is another form of cryptography used in Secure Shell Connections. One-way-hash functions differ from the above two forms of encryption in the sense that they are never meant to be decrypted. They generate a unique value of a fixed length for each input that shows no clear trend which can exploited. This makes them practically impossible to reverse.
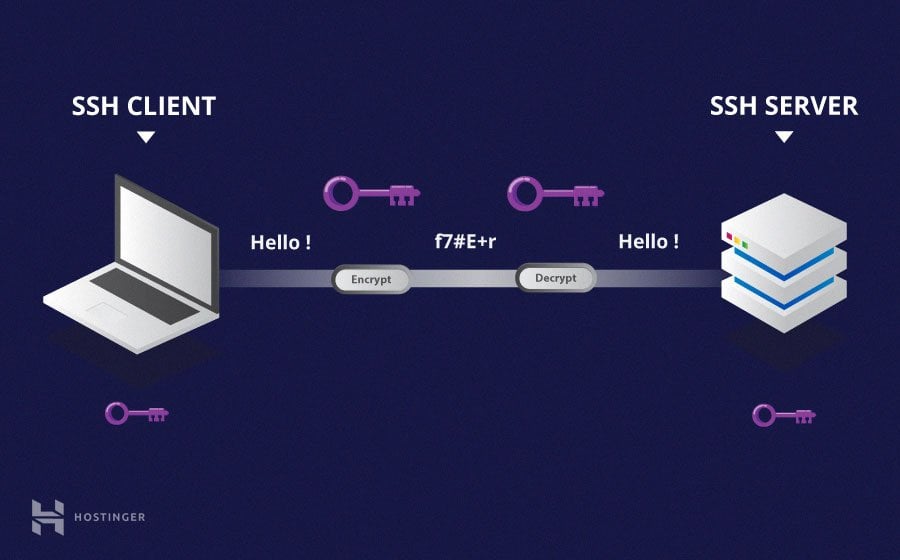
Authenticating the User
-
The final stage before the user is granted access to the server is authenticating his/her credentials. For this, most SSH users use a password. The user is asked to enter the username, followed by the password. These credentials securely pass through the symmetrically encrypted tunnel, so there is no chance of them being captured by a third party.
-
Although passwords are encrypted, it is still not recommended to use passwords for secure connections. This is because many bots can simply brute force easy or default passwords and gain access to your account. Instead, the recommended alternative is SSH Key Pairs.
- hese are a set of asymmetric keys used to authenticate the user without the need of inputting any password.
Resources:
Done by Omar-zoubi