DJANGO forms
HTML Forms:
The form is defined in HTML as a collection of elements inside form tags, containing at least one input element of type=”submit”.
-The form attributes define the HTTP method used to send the data and the destination of the data on the server (action):
-action: The resource/URL where data is to be sent for processing when the form is submitted. If this is not set (or set to an empty string), then the form will be submitted back to the current page URL.
method:
-
The HTTP method used to send the data: post or get.
- The POST method should always be used if the data is going to result in a change to the server’s database because this can be made more resistant to cross-site forgery request attacks.
- The GET method should only be used for forms that don’t change user data (e.g. a search form). It is recommended for when you want to be able to bookmark or share the URL.
Django form handling process:
Django’s form handling uses all of the same techniques that we learned about in previous tutorials (for displaying information about our models): the view gets a request, performs any actions required including reading data from the models, then generates and returns an HTML page.
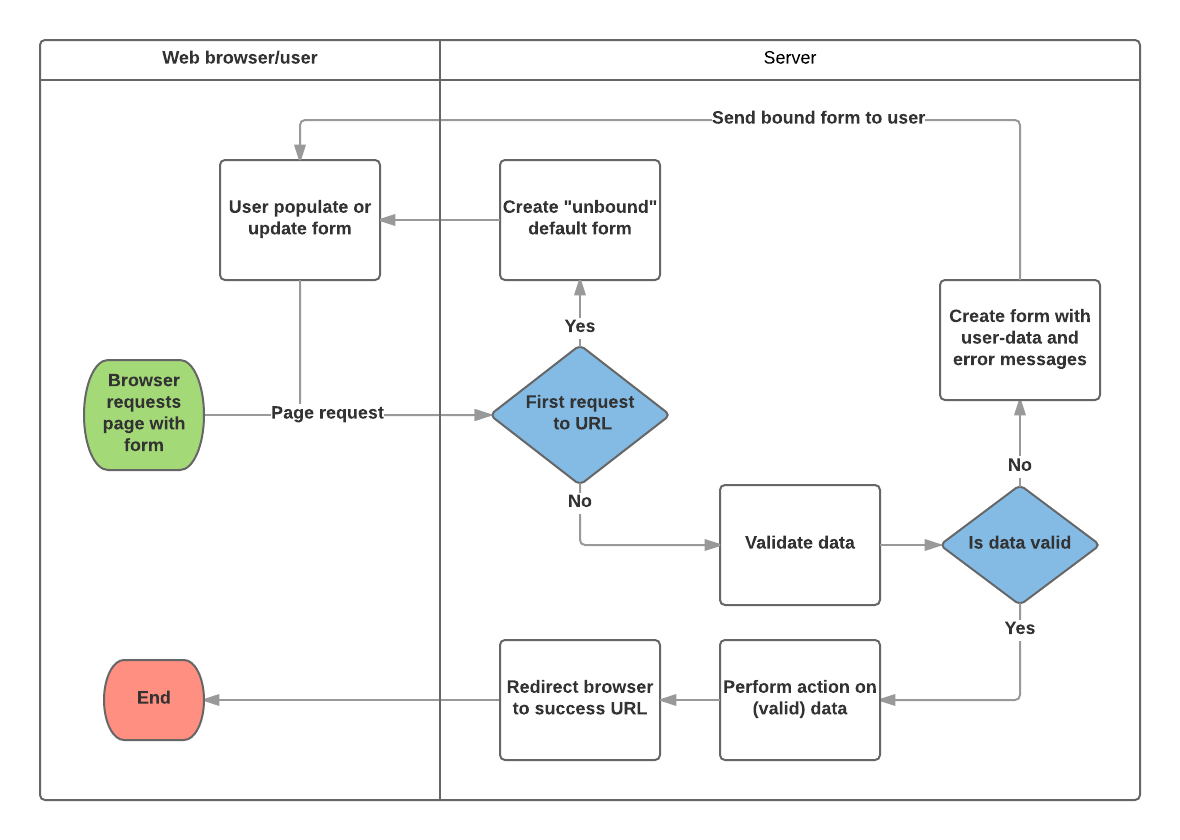
Based on the diagram above, the main things that Django’s form handling does are:
-Display the default form the first time it is requested by the user.
-The form may contain blank fields, or it may be pre-populated with initial values.
-The form is referred to as unbound at this point, because it isn’t associated with any user-entered data.
-Receive data from a submit request and bind it to the form.
-Binding data to the form means that the user-entered data and any errors are available when we need to redisplay the form.
-Clean and validate the data.
-Cleaning the data performs sanitization of the input and converts them into consistent Python types.
-Validation checks that the values are appropriate for the field.
-If any data is invalid, re-display the form, this time with any user populated values and error messages for the problem fields.
-If all data is valid, perform required actions.
-Once all actions are complete, redirect the user to another page.
Resources:
Done by Omar-zoubi